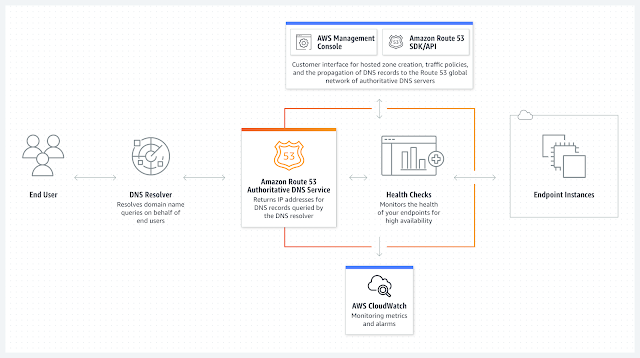
A brief introduction to AWS Route 53 and CloudFront
Route 53 is an Domain Name Server (DNS) service provided by AWS. A DNS is essentially what transforms a URL into an IP address when a network - as you can set local addresses if your on the Intranet, for example. Route 53 is able to deliver seven different routing policies. But it's most basic service includes registering or transferring domain names.
- Simple routing policy: Use for a single resource that performs a given function for your domain—for example, a web server that serves content for the example.com website.
- Weighted routing policy: Use to route traffic to multiple resources in proportions that you specify.
- Latency routing policy: Use when you have resources in multiple AWS Regions and you want to route traffic to the Region that provides the lowest latency.
- Failover routing policy: Use when you want to configure active-passive failover.
- Geolocation routing policy: Use when you want to route traffic based on the location of your users.
- Geoproximity routing policy: Use to route traffic based on the location of your resources and, optionally, shift traffic from resources in one location to resources in another location.
- Multivalue answer routing policy: Use when you want Route 53 to respond
CloudFront is a content delivery network (CDN) service. It essense it is simply a caching service which many ISP's use to minimise their data egress (ie. Netflix or Steam). However it has the advantage of having the Lambda@Edge feature to reduce latency even more. AWS use edge locations to deliver data in a highly available and scalable manner.